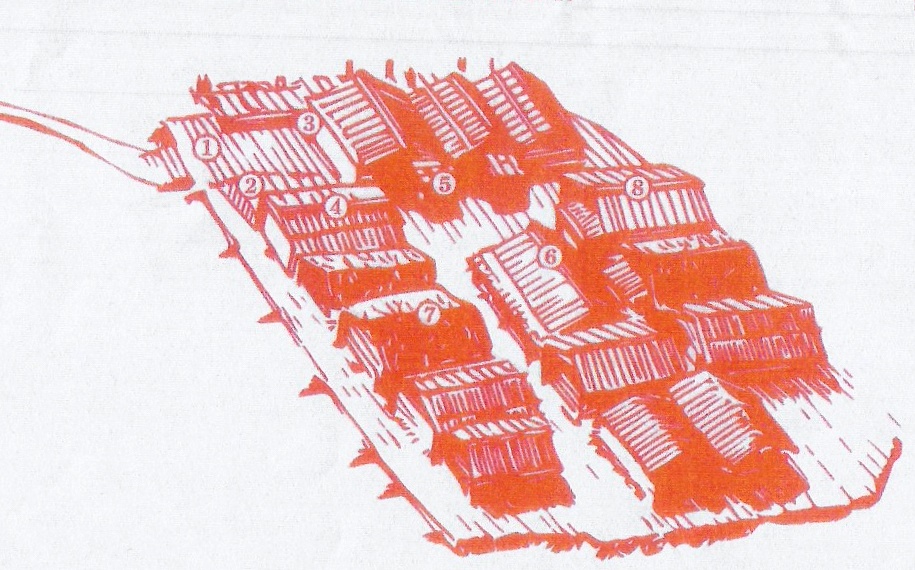


| 1. Basic Wooden Platform:
a platform made on a low island in the lake,
consisting of a lattice covered with a spread of horizontal
logs.
|
5. Household Extension:
located on the right side of the facade of a dwelling house.
Some houses had additional extensions at the sides or at the
back. Tools were stored in these annexes, only some show
signs of the presence of small domestic animals such as
sheep and goats. |
| 2. Defence Construction Fragment: the
settlement was surrounded by defence construction located
along the margin of the platform--a passageway consisting of
chamber-like defensive structures and a defence wall. |
6. Roof: dwellings had gabled ridged roofs.
The covering of the roof consisted of several layers: round
logs or split planks were covered with sheets of birch or
spruce bark that were weighted down with round or split
timbers. The lower ends of the weights are supported by
split timbers put in knees (trees with distinctly bended
roots or branching) not to slide down. |
| 3. Yoke Corner Joint: an archaic form of
joining the corners--the lateral wall of the log structure
are joined to the end wall by means of vertical retaining
poles and horizontal tie-beams or "yoke beams". |
7. Sod Roof: some of the dwelling houses may
have used sod to weigh down the roof construction. |
| 4. Dwelling House: the house used a
rectangular structure of horizontal logs. It is a
chimney-less single-room building with a porch in the end
wall, an entrance on the right side of the porch, and a
small annex also on the right side. At the center of the
living room was a clay stove, but sleeping places and
benches were arranged along the walls. Each house was
occupied by one nuclear family. In each building phase there
were about 16 houses with a population of about 70 to 90
people. |
8. Jeweller's House: people of the lake
fortress had various occupations. Accordning to the
artifacts--crucibles, tools and the semi-finished
products--a jeweller living and worked in one of the houses. |
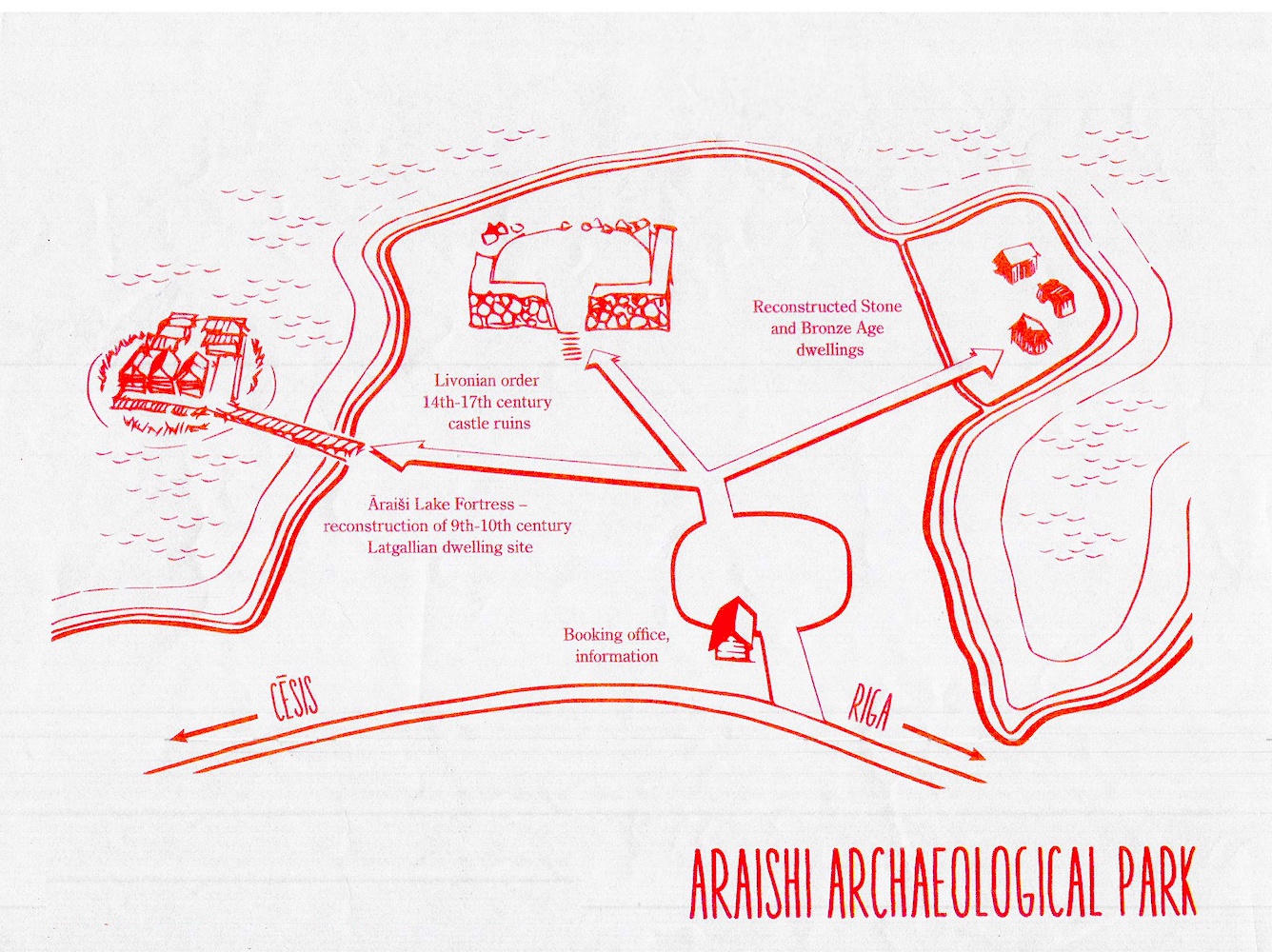
| Araisu Lake Fortress Photos (Click to Enlarge) |
||||
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
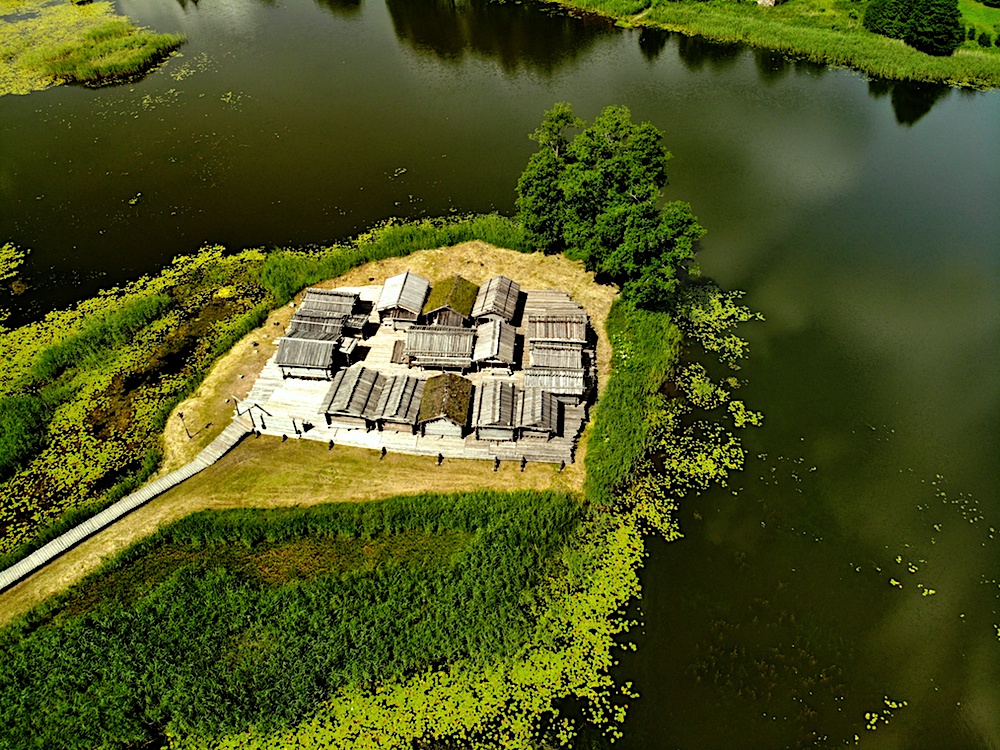
| Aerial View of Araisu Lake
Fortress |
Entrance to Araisu Lake
Fortress |
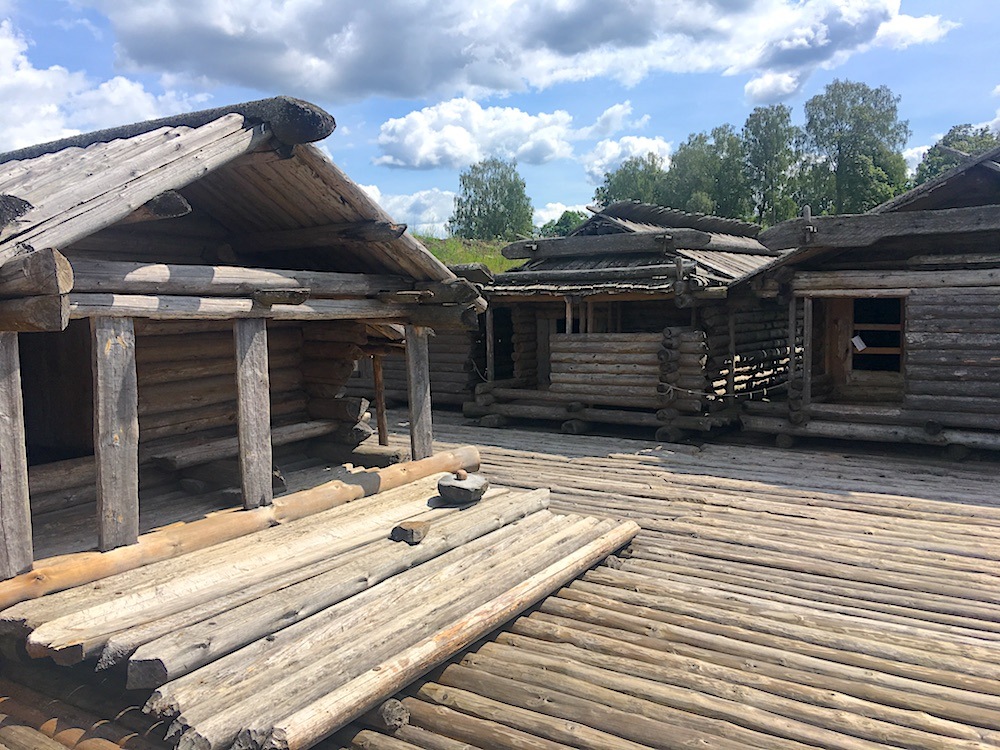
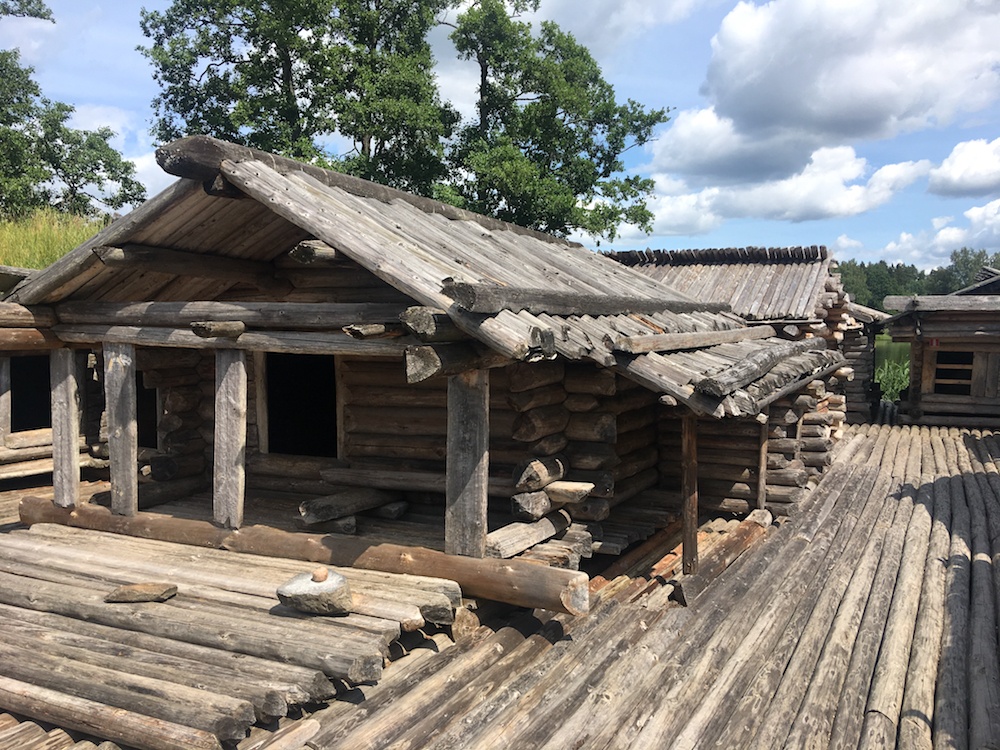
Dwelling Houses with Porches |
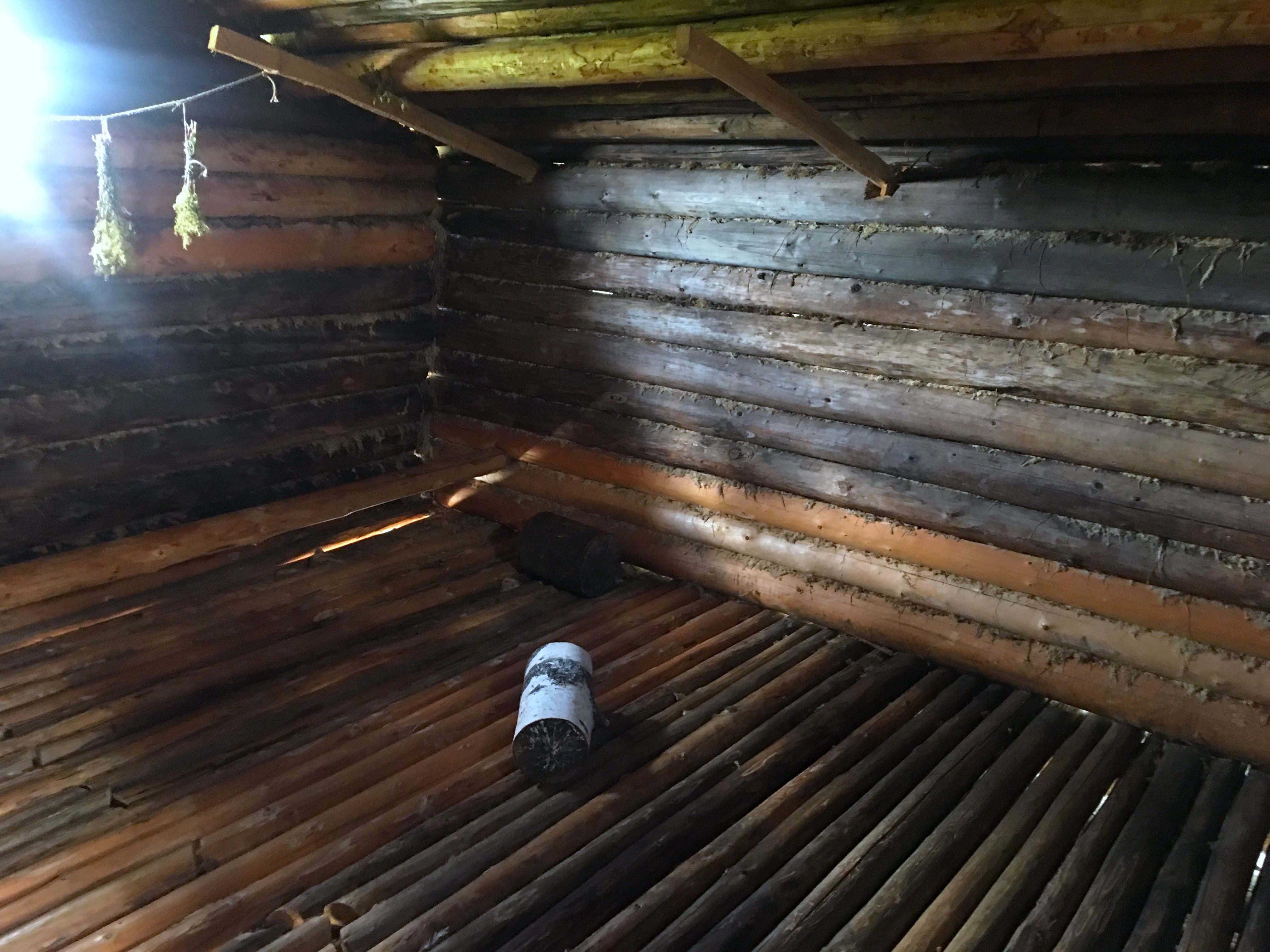
Dwelling House Interior |
Gabled Ridged Roof |
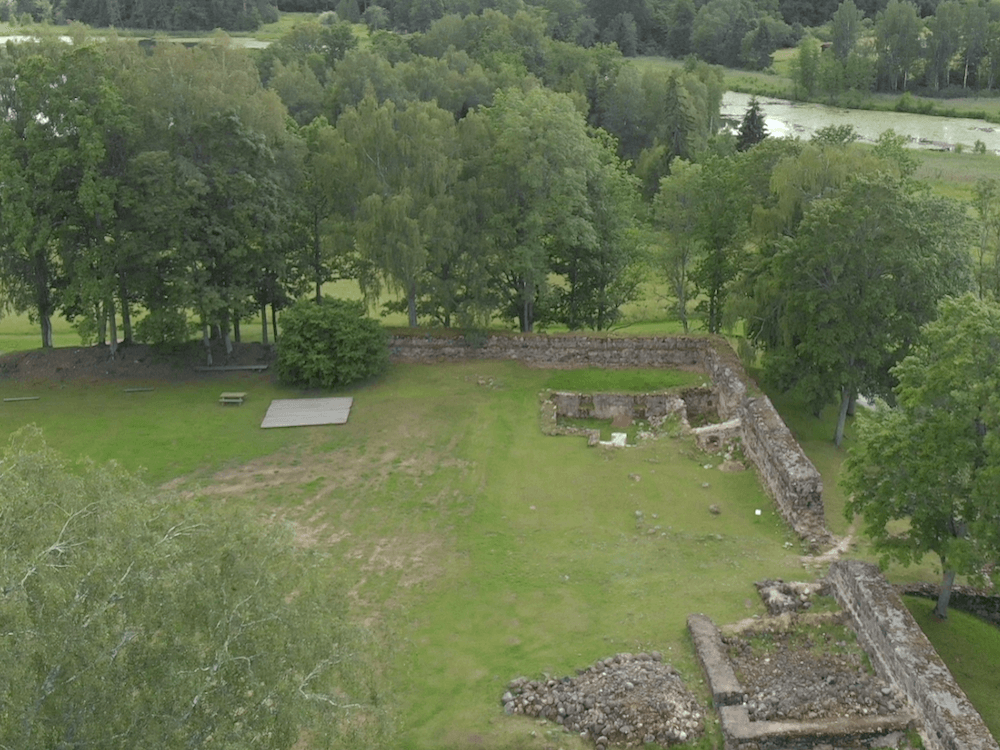
 Araisi stone wall
castle was built in the time of the Livonian order and was
inhabited from the 14th through the 17th century. The castle
occupies the eastern part of the peninsula extending into
Lake Araisi and is separated from the mainland by a dry
ditch, which was spanned by a drawbridge at the castle
gates. The photo to the left shows an
aerial view of the remaining castle walls, while the photo
to the right shows the entrance to the castle. The castle
was built for the master of the Cesis Livonian order for
military as well as domestic purposes. It was destroyed in
the war in the Swedish-Polish war, a part of Thirty Years
War in Europe. In later years the stones of the Middle Ages
castle were used to build Araisi clergyman's house and
Drabesi Manor House buildings. Below is a video overview of
the castle ruins.
Araisi stone wall
castle was built in the time of the Livonian order and was
inhabited from the 14th through the 17th century. The castle
occupies the eastern part of the peninsula extending into
Lake Araisi and is separated from the mainland by a dry
ditch, which was spanned by a drawbridge at the castle
gates. The photo to the left shows an
aerial view of the remaining castle walls, while the photo
to the right shows the entrance to the castle. The castle
was built for the master of the Cesis Livonian order for
military as well as domestic purposes. It was destroyed in
the war in the Swedish-Polish war, a part of Thirty Years
War in Europe. In later years the stones of the Middle Ages
castle were used to build Araisi clergyman's house and
Drabesi Manor House buildings. Below is a video overview of
the castle ruins.
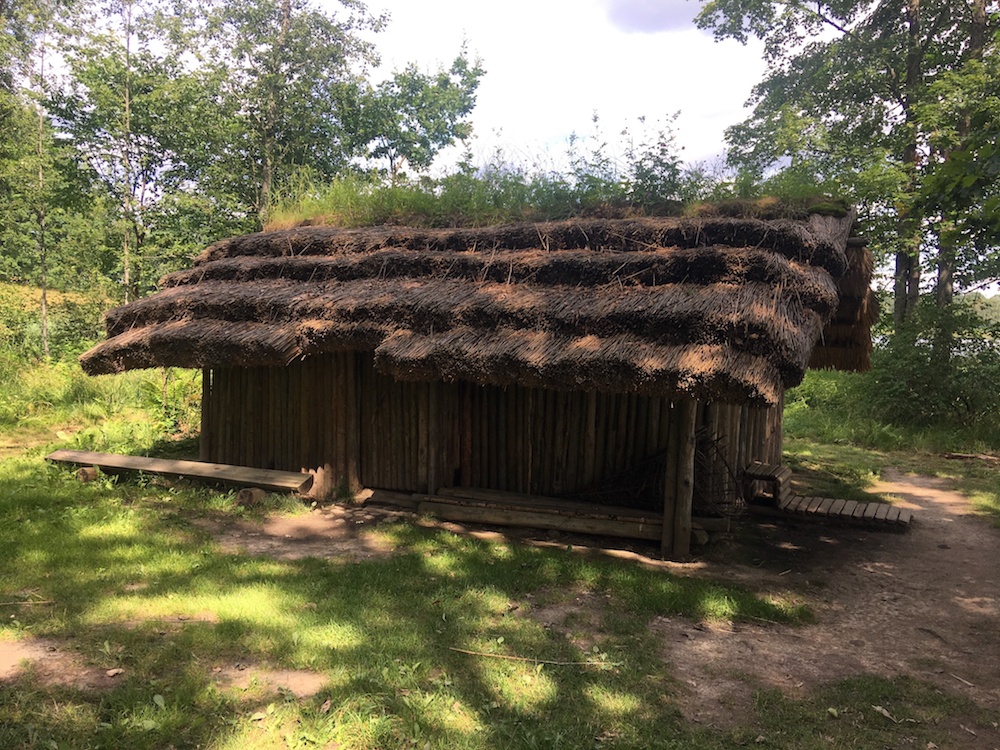 The first
inhabitants in the area of Araisi Lake date from the
Stone Age. The houses on Meitu Island are built as ideal
reconstructions, based on the archeological data about
these types of Stone and Bronze Age houses, obtained in
Latvia and neighboring countries. Below is a video tour
of the site.
The first
inhabitants in the area of Araisi Lake date from the
Stone Age. The houses on Meitu Island are built as ideal
reconstructions, based on the archeological data about
these types of Stone and Bronze Age houses, obtained in
Latvia and neighboring countries. Below is a video tour
of the site.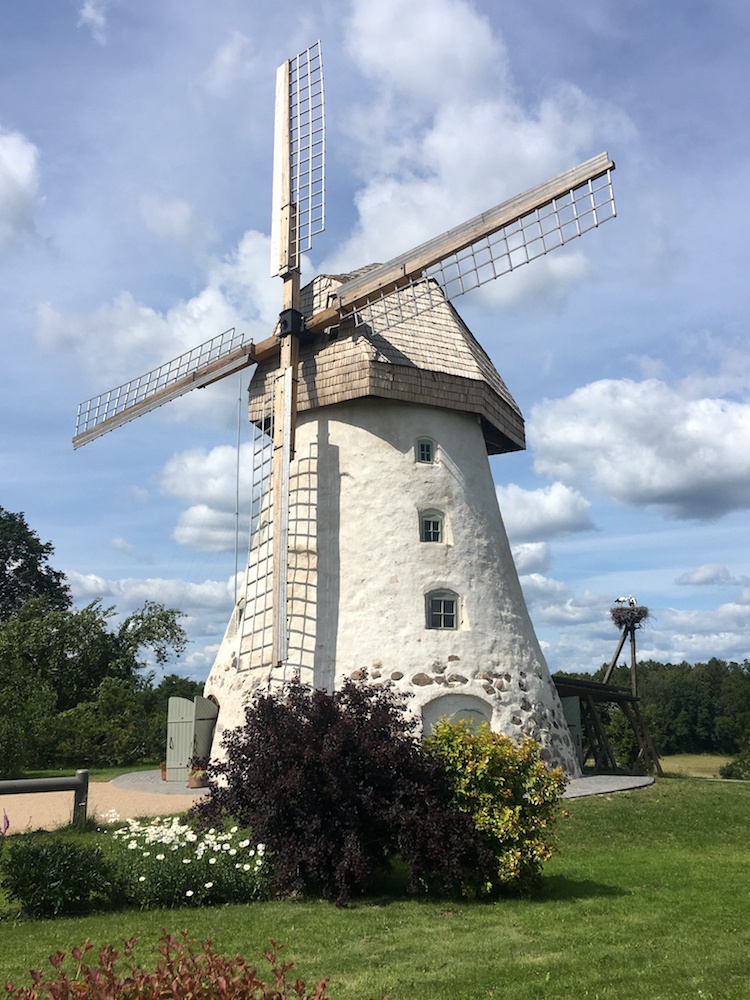
 Before
returning to Amatciems we made one more stop, to visit
the Araisi windmill. This is a Dutch-style windmill,
probably built in 1852, although windmills could be
found in Latvia as early as the 14th century.The photo
to the left shows the exterior of the windmill. Inside,
the structure consists of four stories. The uppermost
floor, shown in the photo to the right, was the spartan
living space.
Before
returning to Amatciems we made one more stop, to visit
the Araisi windmill. This is a Dutch-style windmill,
probably built in 1852, although windmills could be
found in Latvia as early as the 14th century.The photo
to the left shows the exterior of the windmill. Inside,
the structure consists of four stories. The uppermost
floor, shown in the photo to the right, was the spartan
living space.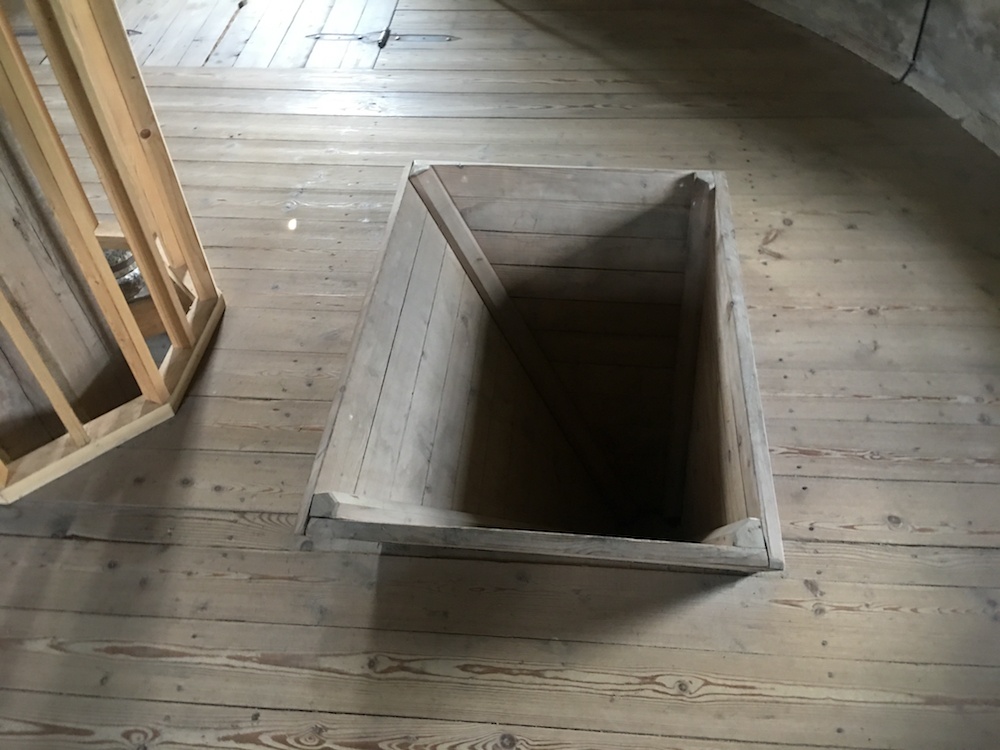 
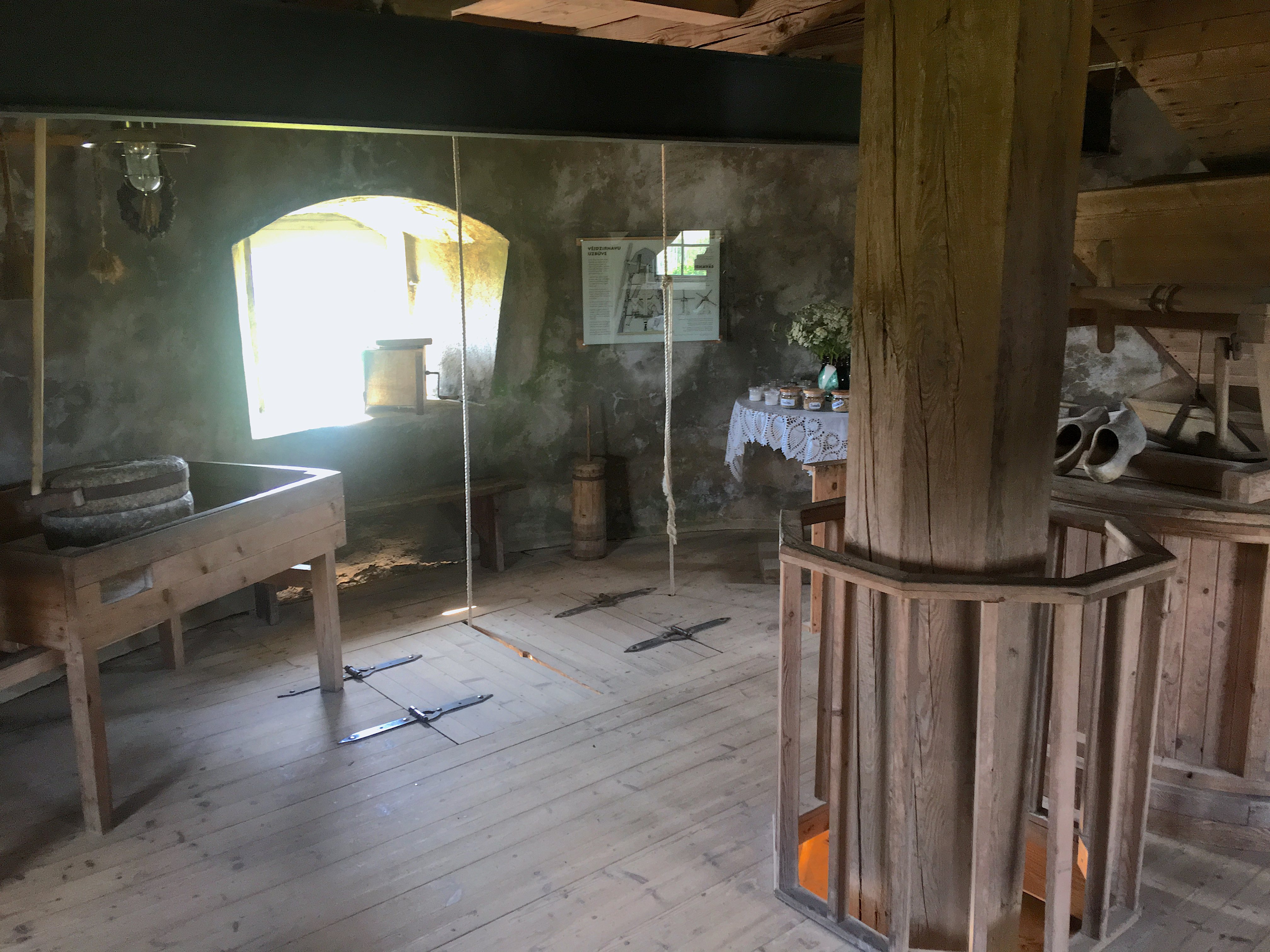
 One floor
below (on the third story) is where the grain was fed
into a chute (photo to the left). It then passed through
the millstones driven by the gears on the second story
(photo to the right). The millstones have carved grooves
and the intermeshing of the stones ground the grain into
a fine flower. Changing of the
millstones was a complicated task requiring special
equipment. The worn millstones were used for house
building and other purposes.
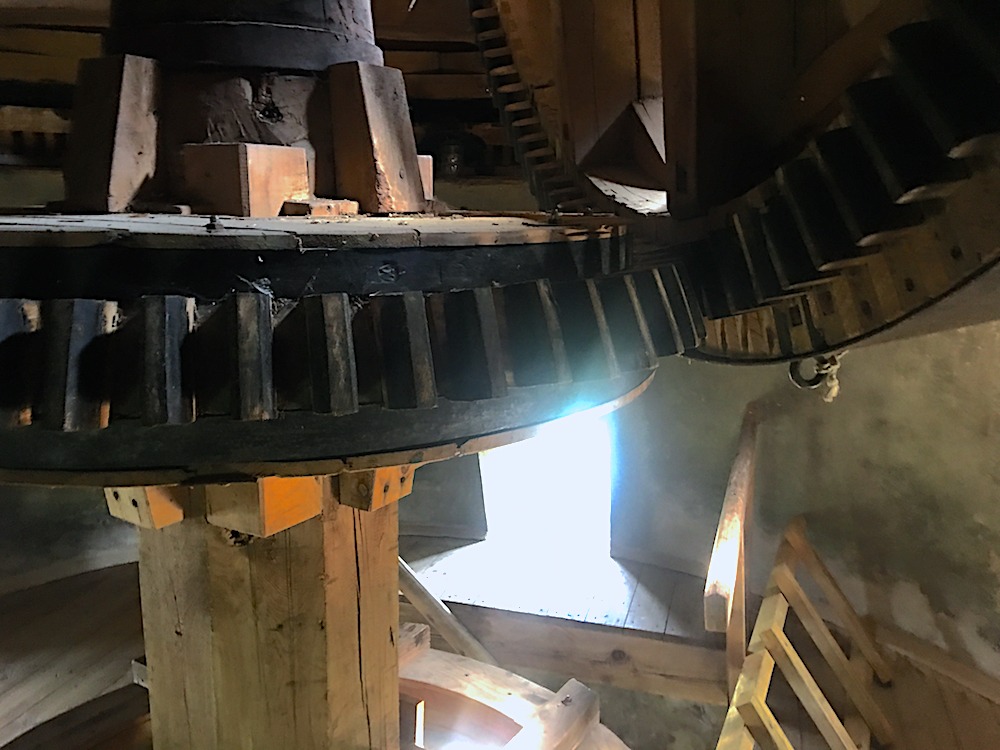
One floor
below (on the third story) is where the grain was fed
into a chute (photo to the left). It then passed through
the millstones driven by the gears on the second story
(photo to the right). The millstones have carved grooves
and the intermeshing of the stones ground the grain into
a fine flower. Changing of the
millstones was a complicated task requiring special
equipment. The worn millstones were used for house
building and other purposes.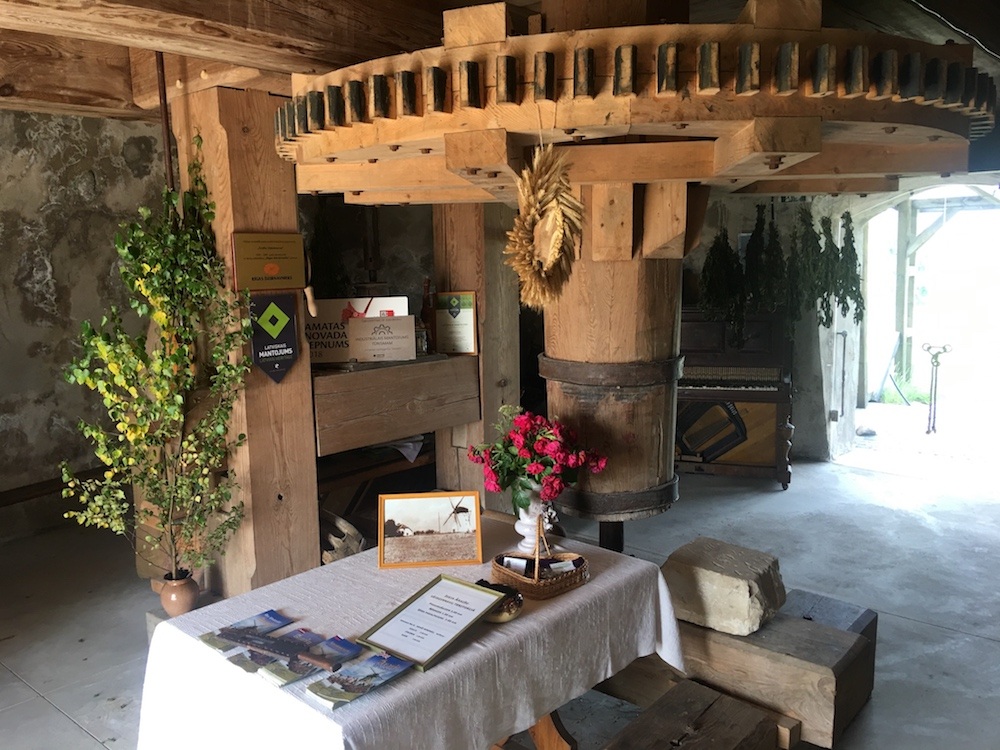  Ultimately
the finished product was poured into sacks on the first
floor. The fineness of the flour could also be adjusted
from this level. The photo to the left shows the chute
where the flour dropped after exiting the millstones,
and where it was bagged.
Ultimately
the finished product was poured into sacks on the first
floor. The fineness of the flour could also be adjusted
from this level. The photo to the left shows the chute
where the flour dropped after exiting the millstones,
and where it was bagged.